Welding series: how to TIG weld (for beginners)

What is welding?
Welding is simply the process of using high heat to join two pieces of metal together; the high heat causes the metal to melt, allowing the pieces to fuse together upon cooling.
There are a number of welding techniques to choose from, depending on the environment, application and metals involved in the welding process.
The most basic and common form of welding class is arc welding (where all beginners start), which includes stick welding, metal inert gas (MIG) welding and tungsten inert gas (TIG) welding.
Here, we take you through the TIG welding process, the welding technique that produces the highest quality welds.
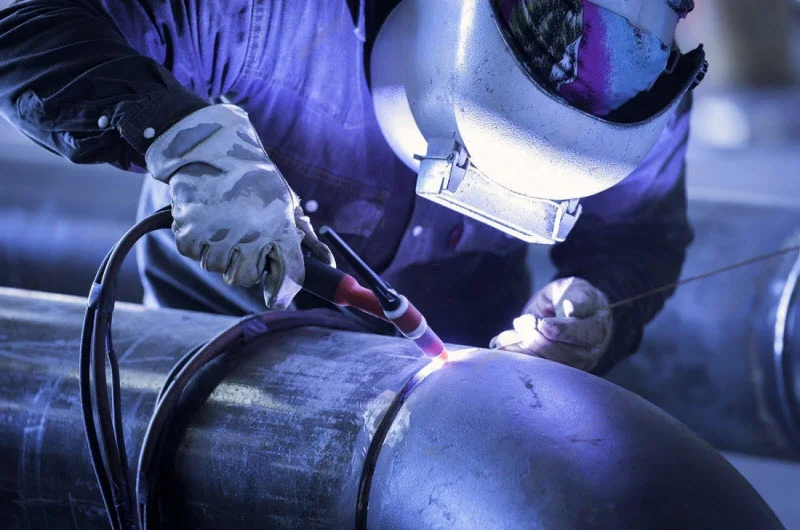

Safety first
Before beginning any welding project, it is vital to ensure all safety measures are in place and you’ve got the right safety gear.
The welding equipment you are using will have specific safety instructions provided by the manufacturer that you must thoroughly review before starting.
You must also have the correct safety equipment on hand to ensure protection from the heat, sparks and UV rays generated during the process. The essentials include:
- Long-sleeved shirt and pants made from fire-retardant materials
- Gloves
- Safety glasses and helmet
- Adequate ventilation if welding indoors (e.g. exhaust).
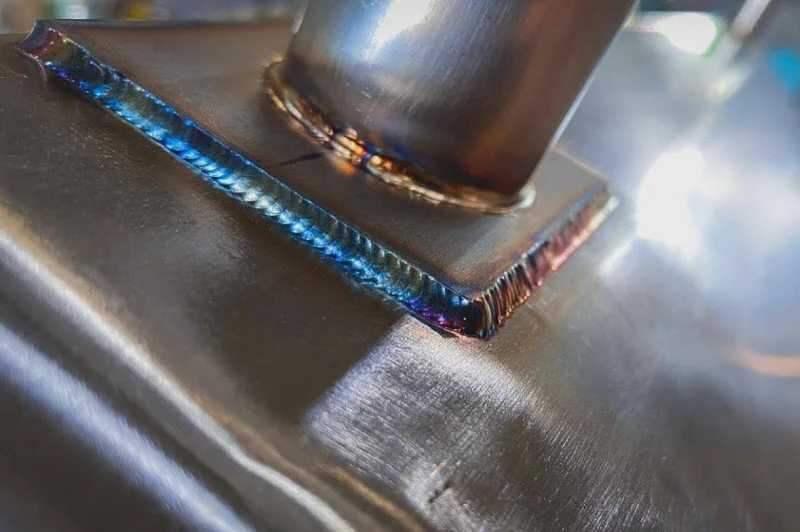

The basics
While TIG welding produces the most precise welds, it is the most difficult welding technique, as the operator must handle both the TIG torch and feed filler material simultaneously while sometimes using a foot pedal, requiring a great deal of dexterity.
TIG welding uses a tungsten (a rare metal) electrode to create an arc that heats the metal workpiece to its melting point. The arc heats the metal, causing the pieces to melt and fuse upon cooling.
During the process, the TIG welding device releases a shielding gas that protects the workpiece from environmental contaminants during the welding process.
Because of the thermal properties of tungsten, an arc can be maintained up to extremely high temperatures without melting the electrode. Tungsten also has a much higher tensile strength as compared to steel.
Advantages and disadvantages
Advantages
- Produces the most precise welds.
- A versatile method that can be used for the widest range of metals, including stainless steel, steel, nickel alloys, aluminium, copper, magnesium, bronze, brass and gold.
- No danger of corrosion created from flux entrapment, as it does not rely on flux material.
- No post-weld cleaning as no slag is created; no spattering is involved.
- A safer alternative to MIG and stick welding as no sparks or hazardous fumes are created in the process.
Disadvantages
- Level of difficulty: Most difficult of the welding techniques.
- Gas requirements: A shielding gas must be used to protect the weld from corrosion while it is hot.
- Not suitable for outdoor use: Due to the use of gas in the process, TIG welding is not recommended for outdoor use.
- Time: TIG welding is a much slower process than stick and MIG welding.
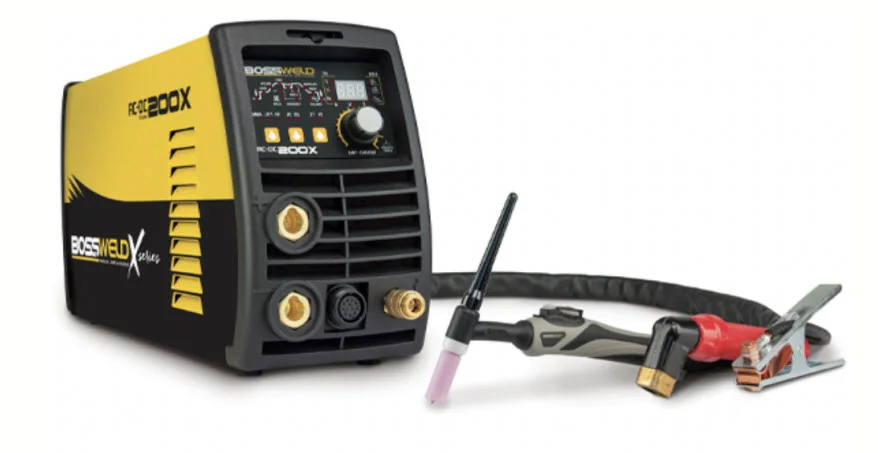

Equipment
Welding device
If you are a beginner, we recommend a multipurpose welding machine that allows you to practise a number of welding techniques, such as stick, TIG and MIG.
Torch
Different torch sizes are available with varying current capacities. The torch case holds the electrode and gas nozzles.
Water cooling system
Some higher-end TIG machines are fitted with water cooling systems, which prevent the torch from being overheated. While these are more efficient than air cooling, they do require additional maintenance.
Tungsten electrode
Tungsten has great electrical and thermal conductivity, as well as a very high melting point, making it highly suitable for TIG electrodes.
Gas nozzle
Gas nozzles made from a thermal-resistant ceramic material must be able to withstand the high welding temperatures used in TIG welding. Various nozzle shapes are available depending on the welding project.
Gas lens
A gas lens is employed for smooth gas flow that will protect the weld pool.
Gas
TIG uses gas to protect the weld from corrosion while it is hot. It is important to choose the right gas for your project. The most commonly used gas for TIG welding is argon (Ar). Argon or argon/helium mixtures can be used for welding all grades.
In some cases, nitrogen or hydrogen can be added to achieve special properties; however, they should not be used when welding martensitic, ferritic or duplex grades.
Oxidizing additions are not used because these destroy the tungsten electrode.
Edcon Steel has a variety of SpeedGas cylinders available for purchase or swap and go, including carbon dioxide, argon and a blended (argon/carbon dioxide/oxygen) gas that is ideal when doing light fabrication work with a TIG welder on carbon steel.
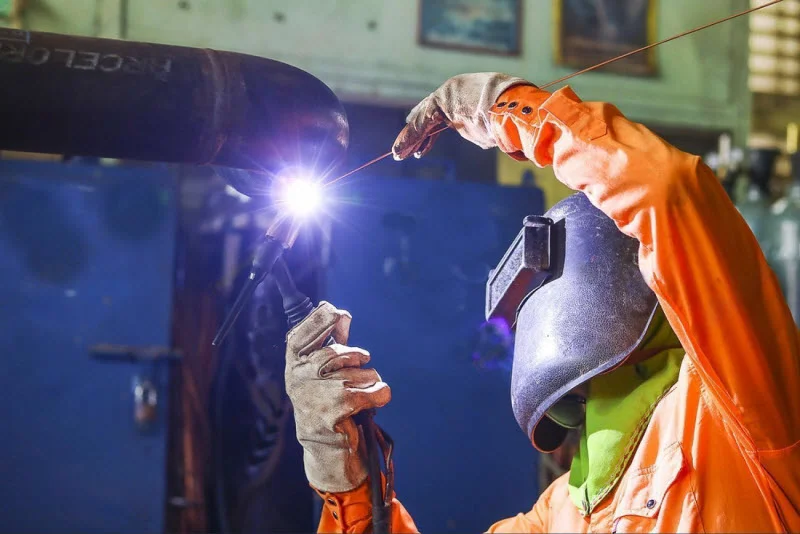

TIG welding techniques
Setting up your welding device should always be done by following the manufacturer’s instructions and ensuring all settings are correct.
Like all welding techniques, TIG welding takes practice.
You should always practise with scrap metal before moving on to welding projects, particularly given the number of functions in TIG welding, such as feeding filler metal, holding the torch correctly and controlling the foot pedal.
Edcon Steel keeps a range of metal and steel offcuts at all our stores that are perfect for practice.
Are you looking for complete steel solutions?
Edcon Steel is Australia’s most comprehensive online steel and metal superstore. We cut and supply steel and metal – in a wide range of shapes, sizes and grades – for all your project needs.
We know metal and steel – and we know our customers appreciate our service and stockholding, so feel free to contact us for your steel or metal solution today.