Galvanised steel tube coatings

When it comes to galvanised steel tube coatings, our friends at Austube Mills know what they’re talking about.
As one of the most recognised and respected manufacturers of certified steel, pipe and tube sections, they specialise in a range of steel coatings.
Here, they delve into galvanised coatings for steel tubes and provide insight into the advantages and disadvantages of various types.
Certain applications can require a specific type of finish, so it is important to discuss this with your steel supplier before ordering.
All steel suppliers, including Edcon Steel, will stock and supply many types of galvanised steel tube, so make sure you’re sourcing the right product for your application.
What are galvanised coatings?
Galvanised coatings on steel, which are part of the metallic coatings range, are typically known to be a long-term, durable and cost-effective means of protecting steel from the effects of corrosion.
The galvanising process generally involves applying zinc to the steel, as it provides protection in corrosive environments with the zinc sacrificing itself instead of the steel.
There are several ways of applying the zinc coating, with each process having its own unique characteristics and performance. These include:
- Hot dip galvanising (HDG)
- Sherardising
- Electroplating or electrogalvanising
- Zinc (thermal) spraying.
Of these, the HDG process is the most popular, as it is quite robust.
Zinc thickness
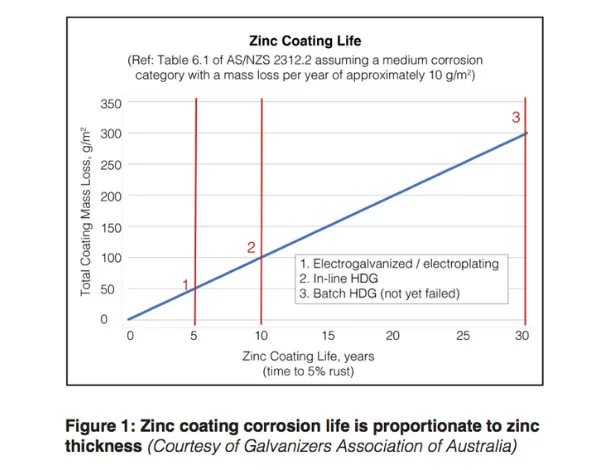
It is well known and scientifically established that for metallic coatings, the zinc thickness is proportional to service life (i.e. durability or life-to-first maintenance in a corrosive environment).
Specifically, if the zinc thickness is doubled, the service life is doubled in corrosive environments. This is recognised in key Australian Standards such as AS/NZS 2312.2 Guide to the protection of structural steel against atmospheric corrosion by the use of protective coatings, Part 2: Hot dip galvanising, reflected in Figure 1.
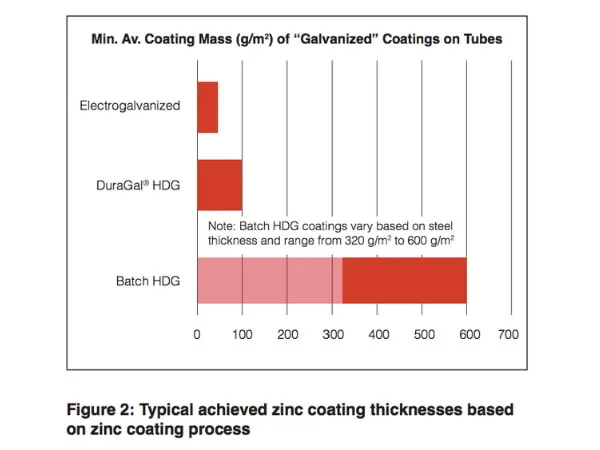
The relative thickness from various metallic (zinc) coating types can be seen in Figure 2, which shows the variety of metallic coatings that can be considered as HDG.
HDG
In-line HDG galvanised (such as DuraGal®) and electrogalvanised tubular products are popular, as they serve a niche in the metallic coatings market for structural applications.
Their benefits from a lower coating thickness include:
– Easier manipulation and bendability, without coating failure (such as flaking)
– Easier weldability
– Maintaining adequate service lives in corrosion environments as described in AS/NZS 2312.2.
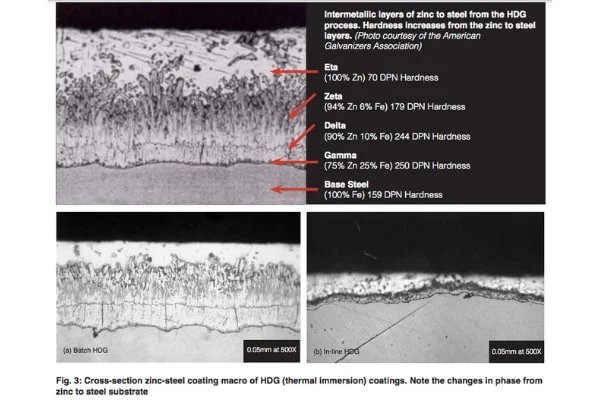
In HDG, the zinc coating is applied by immersing the steel in a molten zinc bath.
This allows for a metallurgical bond to be formed between the steel substrate and the zinc such that, when you analyse the cross-section of the steel and coating, it varies from free zinc to steel with intermediate layers of zinc-steel phases (see Figure 3, which notes steel-coating cross-section macros).
In essence, it is said that the ‘steel and the zinc become one’. Such a trait ensures a good adhesion and abrasion resistance of the zinc to steel as exhibited by the well-known Batch HDG and related In-line HDG galvanising processes.
Other Zinc Coatings
Processes such as thermal spray, zinc-rich paint and electrogalvanising do not exhibit this trait. Though utilising heat, the application of zinc in the thermal spray and similar processes are different from that of batch or in-line HDG galvanising processes.
Electrogalvanising does not have any significant heating requirements and relies on electro-static attraction of zinc to the steel in a cold chemical solution of zinc and can only economically provide thinner zinc coatings. Essentially, electrogalvanising (also known as zinc or electroplating) is a process where zinc is applied using an electrical current. While it does provide some corrosion protection, its thinner coating is not as rust resistant as hot dip galvanising.
A problem arises where there is the market perception that the standards available through electrogalvanised coatings are the same as in-line hot dip galvanised coatings… when they really aren’t.
Are you looking for steel or metal solutions?
Edcon Steel is Australia’s most comprehensive online steel and metal superstore, so if you’re looking for products for your next project, we’ve got you covered. We cut and supply steel and metal – in a wide range of shapes, sizes and grades – for all your project needs.
Read more steel articles to find out more about the steel industry, customer projects and product resources.